Table of Contents
NAD+ drops steadily with age, and many people look for ways to support energy, metabolism, and daily cellular repair. This is where NMN and NR often come in.
Both molecules help raise NAD+, but they follow different steps in the body and may behave a little differently depending on the tissue.
NMN vs NR is a common question for anyone exploring healthy aging or trying to understand how to support natural energy production. Knowing how each precursor works can make your choice easier.
This breakdown gives you the key differences, what current research shows, and what these findings may mean for your health goals.
In this article, you will learn:
-
How NMN and NR work in the body and where they fit in the NAD+ cycle
-
The key differences between the two precursors based on current research
-
What human and animal studies suggest about their benefits and safety
-
How to choose the option that matches your goals, routine, and comfort level
Disclaimer: This article is for information only. Speak with a healthcare professional before using any supplement.
Cellular NAD+ booster with ultra‑pure NMN and Resveratrol, at research‑backed doses.*NMN + Resveratrol
What NAD+ Does in the Body and Why Levels Drop with Age
-v1764018288552.webp)
As you age, NAD+ levels tend to fall due to factors such as inflammation, long-term stress, poor sleep, and general metabolic strain. Research suggests that older adults may have lower NAD+ activity even with a healthy lifestyle (1).
Your body recycles NAD+ through the salvage pathway, where nicotinamide converts back into NMN and then into NAD+ (2). NMN and NR fit directly into this system and help supply the raw materials your cells use each day.
Lower NAD+ levels do not cause a single symptom, but they may influence energy, muscle recovery, and overall metabolic smoothness.
What Is NMN?
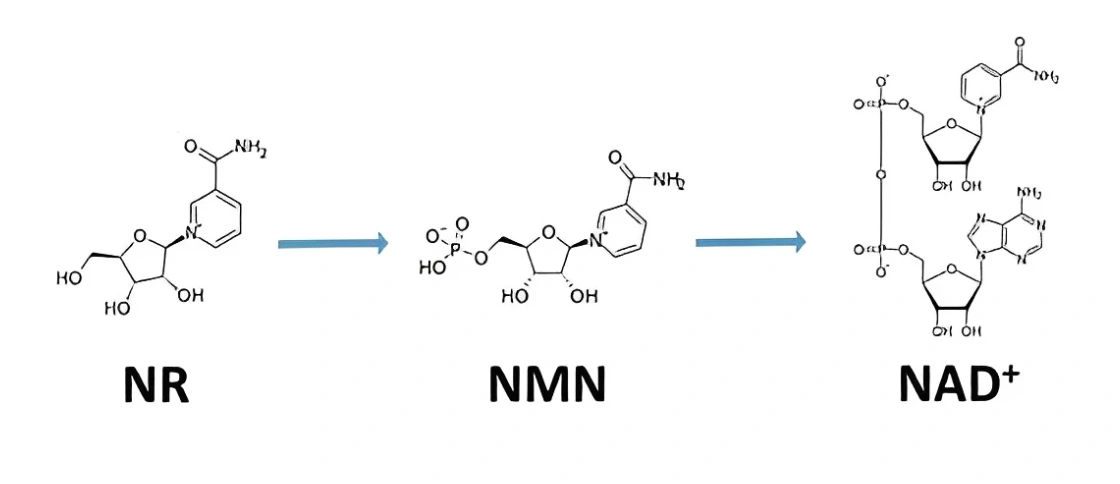 NMN is a precursor your body uses to make NAD+. It is one step before NAD+ in the salvage pathway and carries a phosphate group that gives it a slightly larger structure.
NMN is a precursor your body uses to make NAD+. It is one step before NAD+ in the salvage pathway and carries a phosphate group that gives it a slightly larger structure.
NMN occurs in small amounts in foods such as broccoli, avocado, and edamame. These amounts are low, but the structure of NMN fits the recycling route your cells already use, which is why researchers study it for energy, muscle function, and aging biology.
Scientists are still learning how NMN moves across cell membranes, how much enters the bloodstream intact, and how different tissues use it alongside other B3 compounds.
How the Body Converts NMN Into NAD+
Cells convert NMN into NAD+ through an enzyme called NMNAT. This step supports energy production and repair across many tissues.
NAMPT, another enzyme, works earlier in the pathway by turning nicotinamide into NMN. Together, these enzymes help maintain NAD+ throughout the day.
What Research Says About NMN
Human studies on NMN supplementation suggest that orally administered NMN is generally well tolerated at commonly tested doses. A Japanese trial in healthy adults using 250 mg to 500 mg per day reported increases in NAD+ related markers without serious side effects (3).
Animal research suggests that oral NMN administration may support endurance, mitochondrial activity, and broader metabolic health, although further studies are still needed (4). Early work also explores possible effects on vascular function, including blood flow and arterial stiffness.
Physical performance data remains early, but some small trials suggest possible improvements in walking distance and muscle oxygen use.
What Is NR?
NR is a form of vitamin B3 that supports NAD synthesis through the salvage pathway, which is why nicotinamide riboside often appears in discussions about metabolic pathways and cellular repair. It converts into NMN once inside cells and then into NAD+.
Because NR is smaller than NMN, it enters cells through equilibrative nucleoside transporters. Once inside, NRKs convert it to NMN, and NMNAT completes the final step to NAD+ (5).
This clear transport route has contributed to the number of human trials available on NR.
NR has a long history of use as a dietary ingredient, and many NR supplements are sold under GRAS status in the United States, which supports its presence in many commercial formulas and research settings.
What Research Says About NR
Clinical research consistently suggests that NR supplementation may raise nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) levels in a dose-dependent pattern, with effects varying by dose and duration.
In one trial, a single oral dose increased NAD+ by up to 2.7 times within hours. Longer studies using 300 mg to 1000 mg daily show steady increases over several weeks (6).
NR has shown a good safety profile in the studies available so far. Trials using 1000 mg per day for several weeks have not reported serious side effects so far (7). Research also explores whether NR may influence lipid markers, inflammatory markers, and energy metabolism.
Some early research suggests it may influence endothelial function and blood pressure, although findings vary and more human data is needed. Animal studies also explore whether NR may play a role in brain energy pathways and mitochondrial activity.
NMN + Resveratrol
Cellular NAD+ booster with ultra‑pure NMN and Resveratrol, at research‑backed doses.*
NMN vs NR: Key Differences
NMN and NR both support NAD+ production, but they enter the pathway at different points and use different transport routes. NMN is one step closer to NAD+, while NR converts into NMN first. These structural and pathway differences may influence how each molecule behaves in certain tissues.
Below is a simple comparison table to help you see the main points side by side.
Key takeaways:
NMN sits closer to NAD+ in the salvage pathway, while NR needs one extra step.
NR uses established nucleoside transporters, which explains the strong human data on NAD+ increases.
NMN may use more than one route depending on tissue type, enzyme availability, and transporter activity.
Both lead to the same final molecule, which is why many research findings overlap.
Molecular Structure and Pathway Roles
NMN is larger because it includes a phosphate group, which places it later in the salvage pathway and closer to NAD+.
NR is smaller and resembles a standard nucleoside, which is why it can use existing nucleoside transporters to enter cells. Once NR is inside, NRKs convert it into NMN, and NMNAT completes the final step to NAD+.
Although their starting points differ, both precursors feed into the same recycling loop that helps maintain NAD+ throughout the day.
This shared pathway explains why NR and NMN often show overlapping outcomes in both animal studies and human clinical trials, especially in areas linked to cellular energy.
Bioavailability of NMN and NR
Bioavailability describes how well each precursor is absorbed and how efficiently it enters the salvage pathway. NR uses nucleoside transporters already present in many cells, which helps explain the consistent, dose-dependent increases in NAD+ markers seen in human studies.
NMN may use more than one route. Early research suggests that a transporter called Slc12a8 helps move NMN across the small intestine in mice, and humans carry the same gene, although its activity is still being studied (8).
In some tissues, NMN may convert to NR before uptake and then convert back once inside the cell, which is why both NR administration and NMN supplements are being explored in further research on how the body manages these metabolic routes.
Gut bacteria can also modify both precursors before absorption (9). Because several paths exist, researchers view bioavailability as a shared network rather than a simple competition. This helps explain why people sometimes respond differently to NMN or NR.
Summary: NR follows a predictable entry route through nucleoside transporters. NMN may use several different paths, including transporters, conversion steps, and microbiome support. Both eventually reach the same NAD+ cycle.
How the Body Handles NMN and NR in Different Tissues
Different tissues rely on NMN and NR in their own ways. The liver plays a major role in converting NR to NMN and recycling B3 vitamins, which supports many findings from human studies.
Muscle research in animals suggests that NMN may support endurance and mitochondrial function during exercise, hinting at possible tissue-level differences (10).
The gut expresses high levels of SLC12A8 in mice, and human gene data shows a similar pattern, though the transporter’s exact role in humans remains uncertain. This may influence how quickly NMN appears in circulation after oral intake.
Animal studies also suggest that NR may reach the brain through nucleoside transporters, while NMN may rely on conversion steps before entering neural tissues. More human research is needed to confirm these patterns.
Stability also shapes how each precursor behaves before reaching cells. NMN is sensitive to heat and may convert to nicotinamide if stored improperly, while NR tends to remain stable under a wider range of conditions.
These differences do not change how they function once absorbed but help explain manufacturing and storage practices.
Summary: Different tissues lean on NMN or NR based on transporter activity, local enzymes, and metabolic needs. The liver, muscle, gut, and brain may favor one route at certain times, but both precursors ultimately support the same NAD+ pool.
Legal and Regulatory Differences
NR is sold as a dietary supplement and is considered GRAS in the United States, which gives it a straightforward path in consumer products and research.
NMN is also available as a supplement, but its regulatory situation is more nuanced. It is being studied for potential pharmaceutical use, and this has influenced how some companies choose to label or market their products.
Many regions still allow NMN as a dietary supplement, although rules can differ from place to place. Both NMN and NR continue to be reviewed as more safety and metabolic research becomes available.
Is NMN or NR More Clinically Effective?
-v1764018753835.webp) Current research shows that both NMN and NR can raise NAD+ levels, support metabolic processes, and appear safe in human studies. Their clinical effects overlap, but each has its own evidence based on study design and sample size.
Current research shows that both NMN and NR can raise NAD+ levels, support metabolic processes, and appear safe in human studies. Their clinical effects overlap, but each has its own evidence based on study design and sample size.
NMN Clinical Findings:
Human trials in Japan found that 250 mg to 500 mg of NMN was well tolerated and increased NAD+ related metabolites, supporting its role in the salvage pathway.
Studies in postmenopausal women reported improvements in muscle insulin sensitivity, suggesting a possible metabolic benefit that needs more long-term research (11).
Animal work shows that NMN may support endurance, mitochondrial function, and muscle performance during exercise. These findings highlight potential areas for human follow-up.
Some studies in rodents note better blood flow and reduced arterial stiffness, which points to possible vascular effects that require more human data (12).
NR Clinical Findings:
Multiple human trials show that NR appears to raise NAD+ levels in a dose-dependent pattern, with increases observed at 100 mg, 300 mg, and 1000 mg daily in available studies (13).
NR has a strong safety record in adults, with studies using 1000 mg per day for several weeks reporting no serious side effects (14).
Research on metabolic markers shows mixed but promising signals, including changes in lipid profiles, inflammatory markers, and energy metabolism.
Some trials explore the effect of NR on blood pressure and endothelial function, with early data suggesting possible support for vascular health.
Can You Take NMN and NR Together?
-v1764018710277.webp) Some people take NMN and NR together because they enter the NAD+ pathway at different steps. Research on combined use is still early, so most people start with lower doses of each.
Some people take NMN and NR together because they enter the NAD+ pathway at different steps. Research on combined use is still early, so most people start with lower doses of each.
A combined routine may appeal to those who want to support multiple tissues or pathways at once. NR enters earlier in the cycle, while NMN enters closer to NAD+, which creates a broader approach.
There is no standard combined dose, and long-term studies are still ongoing. If you already take other NAD+ related supplements, it helps to begin with a simple routine.
Which One Should You Choose?
Choosing between NMN and NR often comes down to your goals, comfort with the available studies, and how simple you want your routine to be. Both precursors support the same NAD+ pathway, and both appear well-tolerated in human research.
Choose NR if:
You want the option with more published human trials
You prefer a precursor that uses well-known cellular transporters
You want something stable in storage
You want a form with GRAS status in the United States
Choose NMN if:
You want a precursor that sits one step closer to NAD+
You are interested in early research on muscle activity and physical performance
You prefer a compound studied for gut-related transporter activity
You want something that aligns with emerging metabolic research
Choose Both if:
You want to support multiple steps of the salvage pathway at once
You prefer a broader approach based on tissue differences
You already use NAD+ related supplements like resveratrol or TMG, and want a balanced routine
There is no single correct choice. Both precursors raise NAD+ levels, and the best option is usually the one that fits your habits, budget, and long-term goals.
Should You Test Your NAD+ Levels Before Choosing?
Testing NAD+ levels can help you understand your baseline before choosing NMN or NR. Many tests measure blood NAD+ or related metabolites.
A baseline test can show whether your levels are lower than expected for your age. Some people retest after several months to track changes. Testing is not required, but it can add clarity and help with long-term planning.
Final Words
Both NMN and NR play helpful roles in supporting the body’s natural NAD+ cycle. They follow different steps, use different transport routes, and have different study histories, yet they both lead to the same final molecule your cells rely on for energy and repair.
Current research shows that each precursor can raise NAD+ levels, appears well-tolerated in human trials, and may support areas such as metabolism, muscle function, and cellular health.
The right choice often depends on your routine, your goals, and how you prefer to approach supplementation.
If you are thinking about adding a high-quality NAD+ precursor to your daily habits, a clean formula can make the process simpler. 
Omre NMN + Resveratrol offers a research-guided combination that fits easily into a morning routine and supports the same pathway discussed throughout this article. It is a gentle option if you want a straightforward start.
FAQs
Can NMN turn into NR first?
Yes, some tissues may convert NMN into NR before cellular uptake. After entering the cell, it can convert back into NMN and continue through the salvage pathway. These steps depend on local enzymes and tissue needs.
Does NR enter the brain faster?
NR is small enough to use nucleoside transporters that may help it reach certain tissues, including the brain. Most evidence comes from animal studies, so more human research is needed to confirm timing and distribution.
Will NMN raise NAD+ if Slc12a8 is low?
NMN can still support the salvage pathway even if transporter activity varies. Some tissues may convert NMN to NR outside the cell, absorb NR, and then convert it back into NMN before forming NAD+. This gives the body more than one route to use NMN.
Is sublingual NMN better?
Sublingual forms are designed to bypass some digestive steps, but clear human data comparing sublingual vs oral NMN is still limited. Both forms appear to support increases in NAD+ related markers in early trials.
Do NMN or NR affect sleep?
Most studies do not report sleep-related side effects at common doses. People often take NAD+ precursors in the morning to match natural energy rhythm, but timing can be adjusted based on personal preference.





