Table of Contents
NAD helps your body produce energy, repair damaged DNA, and maintain healthy cells. Research suggests it may also support healthy aging, brain function, metabolism, and muscle performance as levels naturally decline over time.
As interest in longevity grows, many people are asking what NAD actually does and whether supplements make sense. Here is a clear, research-based look at what we know so far.
Key Takeaways:
-
NAD helps your cells produce energy and repair damaged DNA.
-
NAD levels may decline by about 50% between the ages of 40 and 60.
-
Early research suggests NAD precursors like NMN and NR may support aging, brain, and metabolic health.
-
Most findings are promising but still developing, and larger human studies are ongoing.
Cellular NAD+ booster with ultra‑pure NMN and Resveratrol, at research‑backed doses.*NMN + Resveratrol
What Is NAD and Why Does It Matter?
 NAD stands for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. It is a coenzyme found in every living cell. Without it, your cells cannot turn food into usable energy.
NAD stands for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. It is a coenzyme found in every living cell. Without it, your cells cannot turn food into usable energy.
In simple terms, NAD acts like a helper molecule. It supports several key processes:
Converting nutrients into cellular energy
Repairing damaged DNA
Supporting healthy mitochondria, the energy centers of cells
Helping regulate cellular stress responses
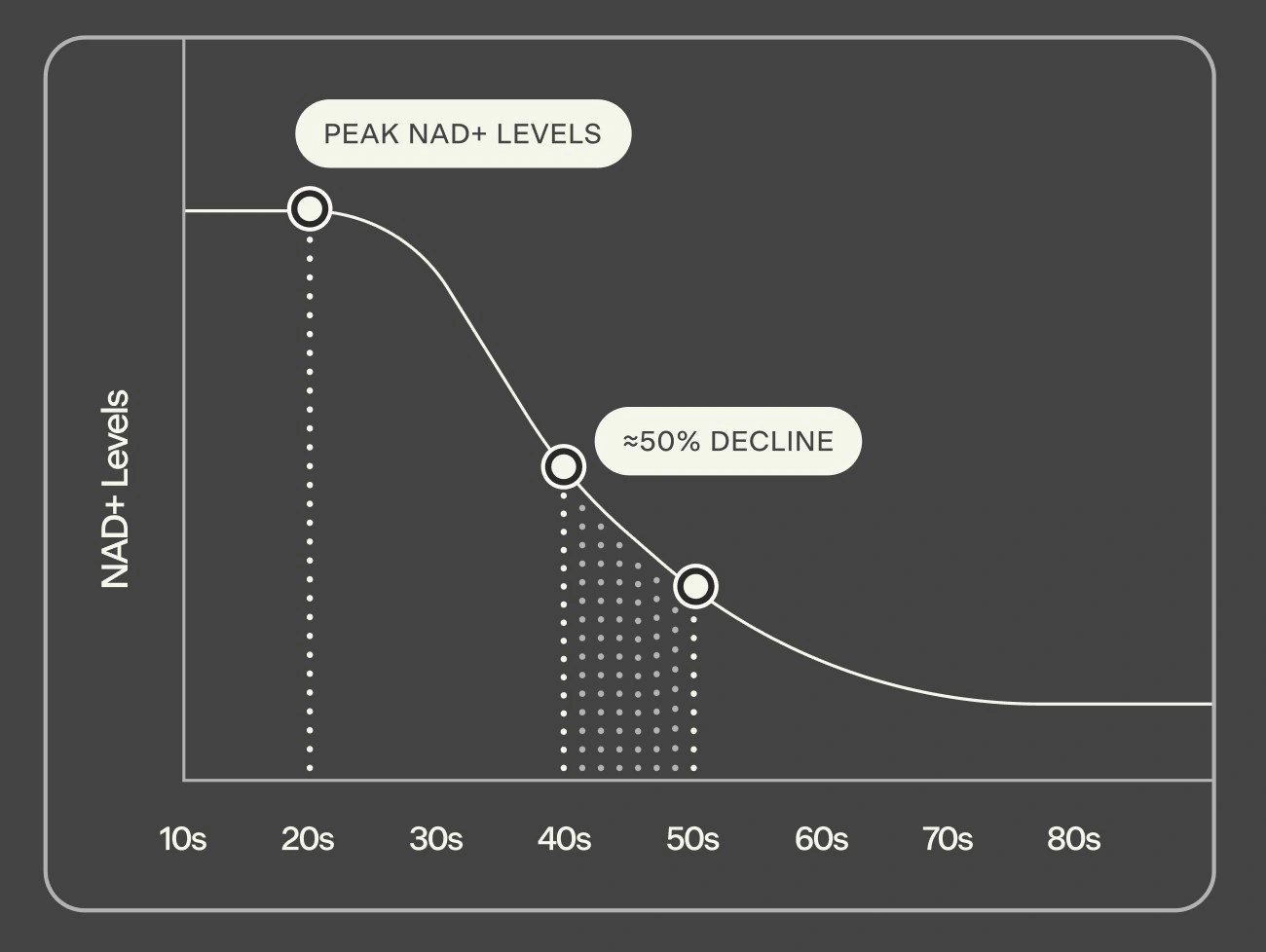
Research suggests NAD levels decline with age. According to studies, NAD+ levels may drop by about 50% between the ages of 40 and 60 (1). This decline is one reason scientists are studying whether restoring NAD levels may support healthy aging.
What Does NAD Help With?
-v1771641577267.webp) NAD primarily helps with energy production, DNA repair, and maintaining healthy cell function. Because these processes affect nearly every organ system, researchers are exploring its potential role in aging, brain health, metabolism, muscle performance, and skin repair.
NAD primarily helps with energy production, DNA repair, and maintaining healthy cell function. Because these processes affect nearly every organ system, researchers are exploring its potential role in aging, brain health, metabolism, muscle performance, and skin repair.
Below is a closer look at areas where NAD is being studied.
May Support Healthy Aging
NAD levels naturally decrease as we get older. Since NAD is involved in energy production and cellular repair, lower levels may be linked to age-related decline.
Animal research has found that restoring NAD levels was associated with longer healthspan and reduced signs of premature aging (2). These findings led researchers to focus on NAD precursors such as NMN and NR in human trials.
Early human research suggests potential benefits in areas such as:
Cardiovascular health in middle-aged and older adults
Mitochondrial function, including in people with heart failure
Skeletal muscle strength and mass
For example, clinical studies have reported improvements in markers related to heart function and muscle performance when NAD precursors were used at research-supported doses (2).
However, larger and longer-term human trials are still ongoing. At this stage, NAD is being studied as a possible support for healthy aging, not a proven anti-aging treatment.
May Help Support Brain and Cognitive Function
Research suggests NAD may help support brain health by reducing nerve inflammation and supporting cellular repair pathways.
Observational findings have reported that people with Parkinson’s disease may have lower NAD levels. In a 2023 clinical trial, participants with Parkinson’s disease took 1,500 milligrams of nicotinamide riboside twice daily (3).
The study found that NAD levels increased and some symptoms showed improvement, though responses varied.
In another study involving individuals with Alzheimer’s-related dementia, daily NAD supplementation was associated with positive changes in certain cognitive measures (4).
While these results are encouraging, they are still early. More research is needed before firm conclusions can be made about NAD and neurodegenerative conditions.
May Support Metabolic Health and Insulin Sensitivity
Metabolic health refers to how well your body manages blood sugar, insulin, cholesterol, and body composition. When these systems do not function well, the risk of conditions such as type 2 diabetes and heart disease increases.
A small 2021 study in postmenopausal adults with prediabetes and excess weight found that taking 250 milligrams of NAD daily for 10 weeks improved insulin sensitivity (5). This suggests NAD may help the body respond to insulin more effectively in certain groups.
Other clinical studies have reported improvements in body composition, lipid levels, exercise capacity, and muscle composition with NAD supplementation (6).
These findings are still considered early but promising. Larger trials will help clarify how meaningful these changes are over time.
NMN + Resveratrol
Cellular NAD+ booster with ultra‑pure NMN and Resveratrol, at research‑backed doses.*
May Support Muscle Function and Physical Performance
NAD plays a direct role in mitochondrial function. Mitochondria produce the energy your muscles rely on for movement and recovery.
Mitochondrial function tends to decline with age. Researchers are studying whether restoring NAD levels may help support muscle strength, endurance, and recovery, especially in older adults (7).
Some clinical research has linked NAD precursor supplementation with improvements in muscle performance and energy metabolism. These effects may be particularly relevant for aging populations and individuals with heart failure, where mitochondrial function is often reduced.
May Help With Skin Health and DNA Repair
One of NAD’s most important roles is supporting DNA repair. Every day, your cells experience damage from normal metabolism and environmental factors such as ultraviolet light.
Because of its role in cellular repair, NAD is being studied for potential skin benefits. Research suggests that increasing NAD availability may help the body repair UV-related skin damage and reduce signs of premature skin aging (8).
Topical NAD formulations have also been studied in conditions such as psoriasis. In these cases, topical application was associated with slowing excessive skin cell multiplication.
It is important to note that topical and oral NAD work differently, and research in both areas is still developing.
More studies are needed before NAD-based treatments can be targeted to specific skin conditions with confidence.
How NAD Supplements Work
-v1771641661074.webp) Most NAD supplements do not contain NAD itself. Instead, they provide precursor compounds that your body can convert into NAD inside cells.
Most NAD supplements do not contain NAD itself. Instead, they provide precursor compounds that your body can convert into NAD inside cells.
Common NAD precursors include:
NMN, nicotinamide mononucleotide
After you take them, these compounds are absorbed and enter cellular pathways that help rebuild NAD levels.
Research has found that specific doses of NMN and NR can raise measurable NAD levels in the blood and tissues, though responses can vary by age, health status, and dose (9).
Because NAD works at the cellular level, changes are not usually felt immediately. The goal is to support the body’s natural repair and energy systems over time.
Who Might Consider NAD Support?
NAD support is often explored by adults interested in healthy aging and long-term cellular health.
Some groups that may consider discussing NAD supplementation with a healthcare professional include:
Adults concerned about age-related decline in energy or recovery
Middle-aged or older adults interested in cardiovascular or metabolic health
Individuals focused on brain health as they age
People looking to support mitochondrial function and muscle performance
Personal health history and medications should always be part of the conversation before starting any supplement.
Are NAD Supplements Safe?
NAD is generally considered safe when used at studied doses. When taken in dosages of up to 1,000 milligrams per day, it has not been shown to harm human health in clinical research (10).
Most studies report that NAD precursors such as NMN and NR are well tolerated. Some individuals may experience mild side effects such as digestive discomfort, especially at higher doses.
In research settings, even higher amounts, such as 1,500 milligrams of NR twice daily, have been used under medical supervision, though this is not typical for general use.
As with any supplement, people who are pregnant, breastfeeding, managing chronic conditions, or taking prescription medications should speak with a qualified healthcare professional before starting NAD support.
Final Words
NAD plays a central role in how your cells produce energy, repair DNA, and respond to stress. Research suggests it may support healthy aging, brain function, metabolic balance, muscle performance, and skin repair, but many findings are still developing.
While early human studies are encouraging, larger and longer-term trials are still needed. For now, NAD supplementation is best viewed as a potential tool for supporting cellular health, not a cure or guaranteed solution. At Omre, we focus on research-backed dosing and carefully selected ingredients. Our NMN + Resveratrol formula is designed to support healthy NAD levels while also supporting cellular resilience through complementary pathways.
At Omre, we focus on research-backed dosing and carefully selected ingredients. Our NMN + Resveratrol formula is designed to support healthy NAD levels while also supporting cellular resilience through complementary pathways.
We prioritize transparency, third-party testing, and clinically aligned amounts so you know exactly what you are taking.
FAQs
What are the main benefits of NAD?
NAD primarily supports cellular energy production and DNA repair. Research also suggests it may help support healthy aging, brain function, metabolic health, and muscle performance, though many areas are still under study.
Does NAD really help with aging?
NAD levels decline with age, and restoring them has been associated with improved cellular function in some studies. Early human research suggests possible support for cardiovascular and muscle health, but larger trials are still needed.
Can NAD improve brain function?
Some research has found that increasing NAD levels may support cellular repair pathways in the brain and may be associated with improvements in certain neurological symptoms. However, more clinical evidence is needed before firm conclusions can be made.
Is NAD good for metabolic health?
Clinical studies have reported improvements in insulin sensitivity and certain metabolic markers in specific groups, such as postmenopausal adults with prediabetes. These findings are promising but still considered early.
What is the difference between NAD, NMN, and NR?
NAD is the active molecule used inside cells. NMN and NR are precursor compounds that your body converts into NAD after supplementation. Most oral supplements use NMN or NR because NAD itself is not easily absorbed directly.





