Table of Contents
If you’re looking to support healthy aging, improve energy levels, or keep your cells functioning at their best, you’ve probably come across nicotinamide (NAM) and NMN.
Both supplements play a role in boosting NAD+—a molecule vital for cellular health—but they do so in slightly different ways.
So, which one is right for you? Whether you’re after glowing skin, better metabolic health, or a sharper mind, this article breaks down the differences, benefits, and science behind nicotinamide and NMN to help you make an informed decision.
NMN + Resveratrol
Cellular NAD+ booster with ultra‑pure NMN and Resveratrol, at research‑backed doses.*
Is Nicotinamide and NMN Same?
Nicotinamide (NAM) and NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) are not the same, but they are closely related as both play a role in producing NAD+, a molecule vital for cellular energy and repair.
Nicotinamide is a form of vitamin B3 that the body can convert into NMN, which is then transformed into NAD+. NMN, on the other hand, is a direct precursor to NAD+ and may raise NAD+ levels more efficiently.
While nicotinamide is often used for general wellness and treating deficiencies, NMN is typically targeted toward anti-aging, energy metabolism, and longevity support.
Both supplements serve distinct purposes, making it important to choose one based on your specific health goals.
What is Nicotinamide?
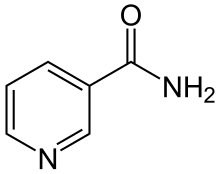 Nicotinamide, also called niacinamide, is a form of vitamin B3 that helps the body produce NAD+, a molecule involved in energy production, DNA repair, and cell health.
Nicotinamide, also called niacinamide, is a form of vitamin B3 that helps the body produce NAD+, a molecule involved in energy production, DNA repair, and cell health.
Nicotinamide is widely used in supplements and skincare products because it’s effective, affordable, and well-tolerated.
It’s also the go-to choice for treating niacin (vitamin B3) deficiency, a condition that can cause skin issues, digestive problems, and even cognitive decline.
Beyond addressing deficiencies, nicotinamide has been studied for its potential role in protecting skin, supporting eye health, and even reducing inflammation.
Unlike some other forms of niacin, it doesn’t cause flushing, making it a popular option for daily supplementation.
How Does Nicotinamide Work in the Body?
Nicotinamide works by converting into NAD+, a coenzyme that supports energy metabolism, DNA repair, and cellular communication.
Once absorbed, nicotinamide gets transformed into NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) and then into NAD+, a molecule that fuels essential processes in every cell.
This pathway keeps energy production running smoothly and helps repair damaged DNA, which is especially important as we age.
Interestingly, nicotinamide also has anti-inflammatory properties. It’s been shown to protect cells from oxidative stress and may even improve the skin’s barrier function—explaining its popularity in skincare.
What is NMN?
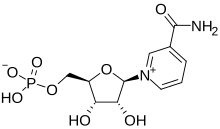 NMN, or nicotinamide mononucleotide, is a direct precursor to NAD+, a molecule that supports cellular energy, DNA repair, and healthy aging.
NMN, or nicotinamide mononucleotide, is a direct precursor to NAD+, a molecule that supports cellular energy, DNA repair, and healthy aging.
Unlike nicotinamide, NMN skips the extra conversion step and turns directly into NAD+, making it a faster and more targeted option for replenishing NAD+ levels.
NMN is often praised for its potential anti-aging effects. Studies have suggested it may improve insulin sensitivity, muscle function, and even brain health—all areas that tend to decline as we get older.
How Does NMN Work in the Body?
NMN works by entering cells through specialized transporters, where it’s quickly converted into NAD+, supporting energy production, cellular repair, and healthy aging.
Because NMN skips the intermediate step required by nicotinamide, it raises NAD+ levels more efficiently. Higher NAD+ levels activate proteins called sirtuins, which are involved in longevity and DNA repair.
Animal studies have even shown that NMN can improve blood vessel function, boost muscle strength, and reduce signs of aging.
While more human studies are underway, early results are promising, especially for those interested in supporting healthy aging.
Potential Health Benefits of Nicotinamide
Studies suggest that nicotinamide may offer several health benefits, especially for skin health, inflammation, and cellular repair.
- May reduce the risk of skin cancer – Research has shown that 500 mg/day could lower the risk of non-melanoma skin cancers by 23% (1).
- Might improve acne and skin health – Studies point to its anti-inflammatory effects, making it useful for treating acne and supporting healthy skin (2).
- May protect against glaucoma – Some studies have found doses of 1.5–3 g/day may enhance retinal function and protect against vision loss (3).
- Could lower phosphorus levels in dialysis patients – Research suggests nicotinamide might help people with kidney disease reduce excess phosphorus in the blood (4).
- May support brain health – Early research indicates it could protect brain cells by reducing oxidative stress and improving mitochondrial function (5).
Potential Health Benefits of NMN
NMN is often linked to longevity and cellular repair, with studies highlighting its potential to improve energy, metabolism, and muscle function.
- May enhance insulin sensitivity – Studies have shown 250 mg/day for 10 weeks improved insulin sensitivity in postmenopausal women with prediabetes (6).
- Might boost physical performance – Research on amateur runners found doses of 300–1200 mg/day improved aerobic capacity over 6 weeks (7).
- Could support muscle function and responsiveness – A study in older adults taking 250 mg/day for 12 weeks reported better muscle responsiveness and reduced fatigue (8).
- May improve heart health – Animal studies suggest NMN might reduce artery stiffness and improve blood vessel function, potentially lowering heart disease risk (9).
- Might protect brain health – Research hints at NMN’s role in reducing oxidative stress, which may lower the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s (10).
- May support longevity – Animal studies suggest NMN might activate sirtuins, proteins linked to DNA repair and lifespan extension, potentially slowing age-related decline (11).
NMN + Resveratrol
Cellular NAD+ booster with ultra‑pure NMN and Resveratrol, at research‑backed doses.*
Safety, Side Effects, and Dosage
Both nicotinamide and NMN are generally considered safe when taken at appropriate doses, but it’s still important to understand their recommended usage and potential side effects.
Nicotinamide
Nicotinamide is typically safe for most people when taken at doses of 500–1,000 mg per day (12). It’s often used for skin health, eye protection, and treating vitamin B3 deficiencies. Higher doses, such as up to 3,000 mg/day, may be used for specific medical purposes under supervision.
Potential side effects:
Mild nausea or upset stomach.
Headaches or dizziness.
Fatigue.
Skin irritation (when used topically).
Liver issues with very high doses (over 3 g/day).
Most side effects occur only at higher doses, and splitting the dosage throughout the day can often help minimize discomfort.
NMN
NMN is also considered safe, with studies showing that doses up to 1,200 mg per day are well-tolerated (13). Many supplements offer doses between 250–500 mg/day, which aligns with research-backed levels for supporting cellular energy and healthy aging.
Potential side effects:
Mild digestive discomfort.
Bloating or gas.
Temporary flushing or warmth (rare).
Allergic reactions (uncommon).
Since NMN is a newer supplement, long-term studies are still ongoing, but short-term data supports its safety profile.
Nicotinamide vs NMN: Who Should Take What?
Choosing between nicotinamide and NMN comes down to personal health goals. Here’s a breakdown to help you decide which might fit your needs better.
Who Should Take Nicotinamide?
Nicotinamide is a great option for people looking to improve skin health, reduce inflammation, or prevent niacin deficiency.
It’s widely used for treating conditions like acne, glaucoma, and high phosphorus levels in kidney patients. Because it’s affordable and readily available, it’s also ideal for anyone who wants a simple way to maintain healthy NAD+ levels without breaking the bank.
Ask yourself:
Do you have skin concerns, like acne or sun damage?
Are you at risk for niacin deficiency?
Have you been diagnosed with glaucoma or kidney-related issues?
Are you looking for a budget-friendly option for general wellness?
If you answered yes to any of these, nicotinamide might be the right choice for you.
Who Should Take NMN?
NMN is best for individuals focused on healthy aging, improving energy, and supporting cellular repair.
It’s popular among people interested in longevity, muscle strength, and metabolic health. Studies also suggest it may benefit older adults or athletes looking to enhance performance.
Ask yourself:
Are you concerned about signs of aging and energy loss?
Do you want to support heart, brain, or muscle function?
Are you interested in longevity and cellular repair?
Do you prefer a supplement specifically designed to raise NAD+ levels?
If these goals align with your needs, NMN could be worth considering.
If you're looking for a supplement that combines NMN with additional support, the OMRE NMN + Resveratrol formula offers a research-backed dose of 500 mg of each ingredient.
This combination not only supports NAD+ production but also activates sirtuins—enzymes linked to longevity and cellular health.
Conclusion
Nicotinamide and NMN both play a role in supporting NAD+ levels, but they cater to different needs.
Nicotinamide is great for skin health, reducing inflammation, and addressing vitamin deficiencies. On the other hand, NMN is ideal for those looking to support anti-aging, energy metabolism, and cellular repair.
If you’re ready to explore NMN’s potential, OMRE NMN + Resveratrol delivers high-purity ingredients at effective doses to help you stay energized and healthy as you age.-v1736356917494.webp) Check availability to see how this supplement could fit into your daily routine.
Check availability to see how this supplement could fit into your daily routine.





