Table of Contents
- What Is TMG?
- Why the Body Uses It
- How TMG Works Inside the Body
- Potential Benefits of TMG Supplements
- TMG for Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Support
- TMG Side Effects and Safety Considerations
- TMG Dosage: How Much Is Typically Used
- Food Sources of TMG
- Who Might Consider TMG Supplementation
- Final Words
- FAQs
TMG supplements are often used to support heart health, exercise performance, and basic cell function. They work by helping the body manage a process called methylation, which plays a role in metabolism and DNA activity.
TMG, also known as trimethylglycine, is a naturally occurring compound found in foods like beets and spinach. It is also available as a supplement for people who want more consistent intake.
Key Takeaways:
-
TMG is a natural compound that helps support methylation and basic cell function.
-
Research suggests it may help manage homocysteine levels, though heart benefits vary.
-
Some people use TMG for exercise support, but results are mixed.
-
Most people tolerate TMG well at moderate doses, with digestive side effects more likely at higher amounts.
What Is TMG
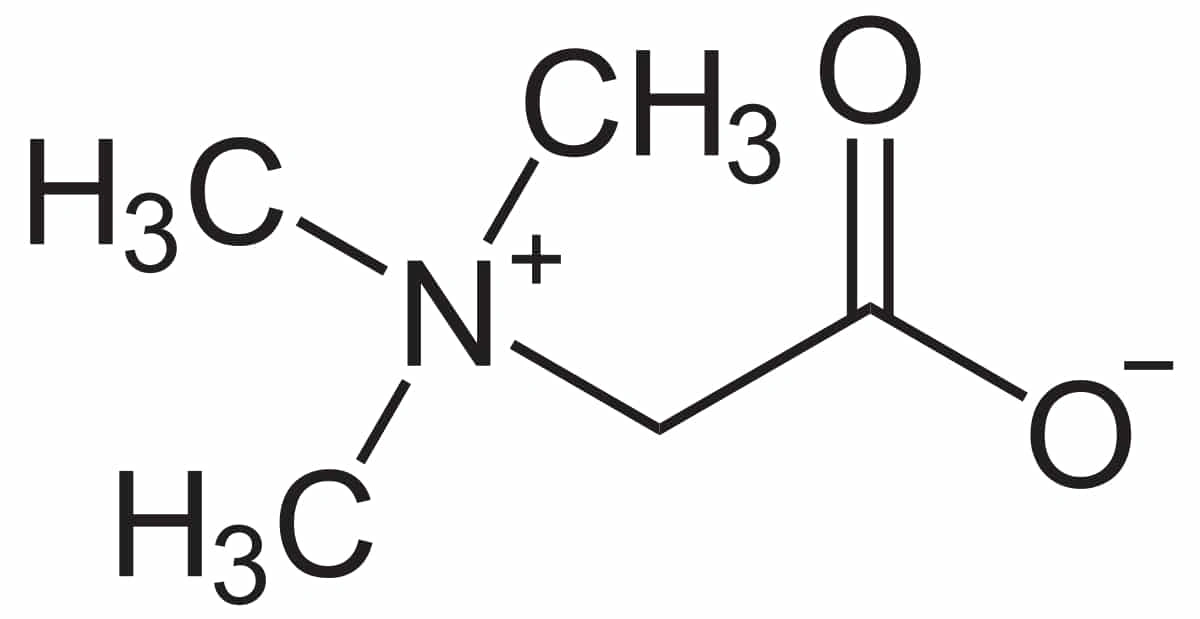
TMG is a naturally occurring compound that helps the body donate methyl groups, which are needed for many everyday chemical reactions. It is also known as betaine or betaine anhydrous and is made from the amino acid glycine with three attached methyl groups.
Your body can produce small amounts of TMG on its own, but most people get it from food. Common sources include beets, whole grains, and certain vegetables. Supplements offer a more concentrated and predictable amount.
Inside the body, TMG mainly supports methylation, a process linked to DNA function, liver health, and amino acid balance.
Because of this role, it has been studied for several areas of health.
Why the Body Uses It
TMG plays a support role rather than acting like a stimulant or medication. Its main value comes from how it helps other systems work more smoothly.
The body uses TMG to:
Donate methyl groups needed for normal cell activity
Help convert homocysteine into methionine
Support liver function and fat metabolism
Assist with the production of certain compounds involved in energy and muscle function
Without enough methyl donors, these processes may become less efficient over time.
How TMG Works Inside the Body
-v1770240827388.webp) TMG works mainly through methylation. This is a basic chemical process that helps turn genes on and off, supports DNA repair, and helps the body process fats and proteins.
TMG works mainly through methylation. This is a basic chemical process that helps turn genes on and off, supports DNA repair, and helps the body process fats and proteins.
One of its most studied roles is helping manage homocysteine levels. Homocysteine is an amino acid that, when elevated, has been linked with higher cardiovascular risk.
TMG helps recycle homocysteine into methionine, which the body can then use for other important functions.
This process may support:
Normal amino acid balance
Healthy liver metabolism
Efficient cellular energy processes
TMG does not force these changes. It provides raw material the body can use as needed.
Potential Benefits of TMG Supplements
-v1770246628090.webp) Research suggests TMG may support several areas of health, though findings are still evolving and not all results are consistent.
Research suggests TMG may support several areas of health, though findings are still evolving and not all results are consistent.
Heart and Cardiovascular Support
TMG is often studied for its effect on homocysteine. Research has found that taking around 3 to 4 grams of TMG per day can lower homocysteine levels in many adults (1). This effect has been observed without major changes in blood pressure or triglycerides.
However, lowering homocysteine does not always lead to better heart outcomes. Some clinical findings suggest that while homocysteine levels improve, this does not automatically reduce heart disease risk.
There is also mixed evidence around cholesterol. Some reports have noted small increases in total and LDL cholesterol in certain people (2).
Because of this, TMG may be helpful for some individuals but should be used thoughtfully, especially by those already managing cholesterol levels.
Exercise Performance and Muscle Function
Athletes often use TMG to support strength, power, and repeated sprint ability. In human trials, doses around 2 grams per day taken for several weeks have been associated with modest improvements in muscle strength and short burst performance (3).
Researchers believe this may relate to TMG’s role in creatine production and protein synthesis, both of which support muscle energy (4).
That said, not all studies show benefits. Some trials report no meaningful improvement in endurance or strength compared to placebo (5).
Because results vary, TMG should not be seen as a guaranteed performance enhancer. Individual response appears to matter.
Insulin Sensitivity and Metabolic Health
Insulin resistance happens when the body does not respond well to insulin, making it harder to manage blood sugar levels. Some population data has linked higher dietary intake of betaine and choline with better insulin sensitivity (6).
Animal research has also reported improved fat metabolism and lower insulin resistance when TMG was added to a high-fat diet (7). These findings help explain possible mechanisms but do not confirm the same effect in humans.
Human evidence is still limited, and more controlled trials are needed before firm conclusions can be drawn.
Mood and Brain Chemistry Support
TMG has been studied alongside SAMe, a compound sometimes used to support mood. Research has found that adding TMG to SAMe supplementation may enhance its effects in people with mild to moderate depression (8).
This may relate to methylation support and homocysteine balance, both of which are linked to brain chemistry. Some reports also suggest a connection between elevated homocysteine levels and mood changes.
TMG is not a treatment for depression or anxiety. Any mental health concerns should always be discussed with a qualified healthcare professional.
TMG for Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Support
TMG has been studied for its potential role in reducing low-grade inflammation and oxidative stress. Research has found that TMG can help support normal inflammatory balance by influencing pathways linked to methylation and amino acid metabolism.
TMG also appears to support the body’s antioxidant defenses. By helping cells manage metabolic stress more efficiently, it may reduce the buildup of harmful byproducts that can damage tissues over time.
These effects are still being studied and are best viewed as supportive rather than therapeutic.
TMG Side Effects and Safety Considerations
TMG is generally considered well-tolerated when used in typical supplemental amounts. Most side effects, when they occur, are related to digestion and are more common at higher doses (9).
Possible side effects may include:
Nausea or stomach discomfort
Bloating or cramps
Diarrhea
Vomiting, usually at higher intakes
In rare cases, very high doses may raise methionine levels in the blood. TMG is not recommended for children or during pregnancy or breastfeeding due to limited safety data.
Anyone with existing medical conditions should speak with a healthcare professional before use.
TMG Dosage: How Much Is Typically Used
 TMG supplements are commonly taken in doses ranging from about 500 mg to 3,000 mg per day, often divided into smaller servings.
TMG supplements are commonly taken in doses ranging from about 500 mg to 3,000 mg per day, often divided into smaller servings.
Clinical research has used doses up to 4 grams per day for homocysteine support, with some studies reporting intakes as high as 9 grams under supervision (10).
Most people start with a lower amount to assess tolerance, then adjust as needed. Higher doses are not always better and may increase the chance of digestive side effects.
Food Sources of TMG
TMG is naturally found in a variety of everyday foods, especially plant-based options.
Common sources include:
Wheat bran and wheat germ
Spinach
Quinoa
Beets
Shrimp
Whole wheat bread
Cooking methods like boiling can lower TMG content, so preparation matters.
Who Might Consider TMG Supplementation
TMG supplements may be considered by people looking to support basic metabolic and cellular processes.
This may include:
Adults interested in methylation support
People monitoring homocysteine levels
Athletes exploring muscle performance support
Those with low dietary intake of TMG-rich foods
TMG is not necessary for everyone and should be used based on individual needs.
Final Words
TMG is a naturally occurring compound that supports methylation, amino acid balance, and basic cellular function.
Research suggests it may help with homocysteine management, exercise performance, and metabolic health, though results vary between individuals.
Like many supplements, TMG works best as part of a balanced approach that includes diet, lifestyle, and professional guidance. Ongoing research continues to clarify where it fits best.
FAQs
What is TMG used for in supplements?
TMG is used to support methylation, homocysteine balance, and basic metabolic processes. It is also explored for exercise and cellular support.
Is TMG good for methylation support?
TMG acts as a methyl donor, which helps the body carry out normal methylation reactions. This role is well established, though individual needs vary.
Can TMG lower homocysteine levels?
Research has found that doses around 3 to 4 grams per day can reduce homocysteine levels in many adults. Lower homocysteine does not always mean improved heart outcomes.
Does TMG help with workouts?
Some studies have reported modest improvements in strength and short burst performance with doses around 2 grams per day. Other studies show no clear benefit.
Are there side effects of taking TMG daily?
Most side effects are digestive and dose-related. Using moderate amounts and splitting doses can help reduce discomfort.



