Nicotinamide Riboside Benefits for NAD+, Aging, and Energy
Updated on Feb 26, 2026

Table of contents
Nicotinamide riboside is a form of vitamin B3 that has gained attention for its role in supporting NAD+ levels, which naturally decline with age.
Interest in NR comes from its connection to cellular energy, repair processes, and healthy aging, not from quick fixes or dramatic claims.
The research is still growing, but early human studies offer useful clues about how NR may support normal body functions over time.
Disclaimer: This content is for educational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional before starting any dietary supplement.
What Is Nicotinamide Riboside (NR)?
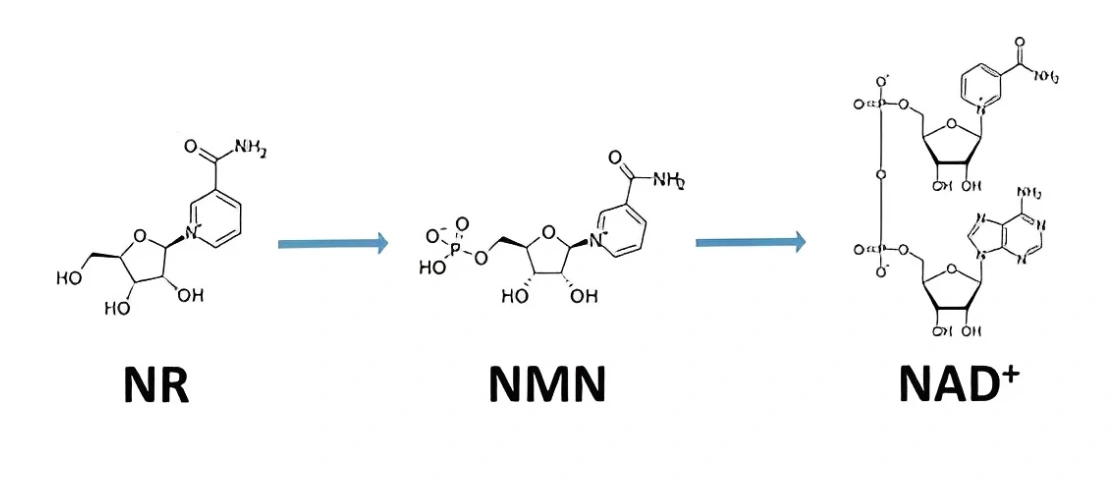 Nicotinamide riboside is a vitamin B3 compound that the body can use to make NAD+, a molecule needed for cellular energy and repair.
Nicotinamide riboside is a vitamin B3 compound that the body can use to make NAD+, a molecule needed for cellular energy and repair.
NR belongs to the same vitamin family as niacin and nicotinamide. Once consumed, it is converted inside the body into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, often shortened to NAD+. NAD+ is found in every cell and plays a role in how cells produce energy and respond to stress.
Unlike some other forms of vitamin B3, NR appears to increase NAD+ levels without causing flushing in most people (1).
Small amounts of NR are found naturally in foods like milk and fermented products, but supplements provide much higher and more consistent amounts.
Why NAD+ Matters for the Body
NAD+ supports basic cellular functions that keep the body working as it should. As people age, NAD+ levels tend to drop, which may affect how well cells handle daily wear and tear.
NAD+ is involved in many normal processes, including:
-
Turning nutrients into usable cellular energy
-
Supporting DNA repair during normal cell activity
-
Helping cells respond to oxidative and metabolic stress
-
Regulating enzymes linked to cellular maintenance
Because every cell depends on NAD+, even modest changes in its availability may influence how the body adapts to aging and physical stress.
Potential Nicotinamide Riboside Benefits
-v1766690630400.webp) Research on nicotinamide riboside is ongoing. Most findings come from small human trials and supporting laboratory studies. The sections below describe what NR may support based on current evidence, not guaranteed outcomes.
Research on nicotinamide riboside is ongoing. Most findings come from small human trials and supporting laboratory studies. The sections below describe what NR may support based on current evidence, not guaranteed outcomes.
1. May Raise NAD+ Levels Efficiently
Human studies have shown that nicotinamide riboside supplementation increases NAD+ levels in the blood (2). This confirms that NR works as a usable NAD+ precursor in people.
NR appears to convert into NAD+ more readily than some other vitamin B3 forms (3). This matters because consistent NAD+ availability supports daily cellular activity rather than short spikes.
Maintaining steady NAD+ levels may help cells meet energy demands, especially in tissues that rely heavily on metabolism.
2. May Support Healthy Aging Pathways
NAD+ activates enzyme families such as sirtuins and PARPs, which are involved in DNA repair and cellular signaling (4). These enzymes help cells respond to normal damage that occurs over time.
DNA repair is part of routine cell maintenance. When this process works well, cells may remain functional longer. Researchers are studying how this activity relates to age-associated changes in the body.
While these pathways are well documented, their long-term impact in humans continues to be studied.
3. Brain and Nervous System Support
Brain and nerve cells have high energy demands. NAD+ plays a role in supporting energy metabolism in these tissues.
Human studies have reported reduced markers linked to neurodegeneration after NR supplementation, along with increased NAD+ levels (5).
This does not mean NR treats or prevents neurological disease. Larger and longer studies are still needed to understand how NAD+ support affects brain health over time.
4. Cardiovascular Health Support
In studies involving middle-aged and older adults, daily NR intake was associated with changes in markers related to vascular function, such as arterial flexibility, in controlled research settings (6). Both measures relate to how flexible blood vessels remain with age.
Vascular flexibility matters because stiff arteries place more strain on the heart. NAD+ is involved in cellular processes that affect blood vessel function.
These findings are promising but are not yet considered definitive clinical guidance.
5. Muscle Function and Physical Performance
A small human study in older men found that NR supplementation was linked to improved markers related to skeletal muscle health (7). Muscle tissue relies heavily on cellular energy production.
Preclinical studies also suggest NR may support muscle function and physical performance during aging (8). These findings help explain why NAD+ availability matters for muscle maintenance.
More human research is needed to understand how this translates to daily strength or mobility.
6. Inflammation and Immune Response
Several studies have observed reductions in inflammatory cytokines following NR supplementation (9). Cytokines are signaling molecules involved in immune responses.
Low grade inflammation often increases with age. NAD+ supports cellular defense systems that help regulate inflammatory signaling.
These effects appear modest and are still being explored in clinical settings.
7. Metabolic Health and Weight Regulation
Animal studies suggest NR intake may improve insulin sensitivity and reduce fat gain under certain conditions (10). These findings point to NAD+ involvement in metabolic regulation.
A large review involving over 5,000 people reported a modest reduction in body mass index among those using NAD+ precursor supplements, including NR (11).
NAD+ supports metabolic signaling, but supplementation alone is not a substitute for diet or lifestyle factors.
8. Skin Health and Cellular Repair
Ultraviolet exposure can damage DNA in skin cells. NAD+ plays a role in cellular repair mechanisms that respond to this damage (12).
Observational research has explored how NAD+ availability relates to cellular repair processes in skin. These findings are early and do not imply disease prevention or reduced cancer risk (13)
The focus remains on NAD+ supporting normal skin cell maintenance.
9. Circadian Rhythm and Jet Lag Support
NAD+ helps regulate circadian rhythms, which control sleep and wake cycles (14). These rhythms influence energy levels and daily biological timing.
Supporting NAD+ levels may help the body adapt to disrupted schedules, such as travel across time zones or shift work.
Research in this area is still developing, but it highlights the broad role NAD+ plays in daily biological regulation.
Food Sources of Nicotinamide Riboside
-v1766690723455.webp) Nicotinamide riboside is found naturally in small amounts in certain foods, mainly those that come from milk or fermentation (15). These sources contribute modest levels and are not comparable to supplemental doses.
Nicotinamide riboside is found naturally in small amounts in certain foods, mainly those that come from milk or fermentation (15). These sources contribute modest levels and are not comparable to supplemental doses.
-
Cow’s milk, which contains one of the highest known dietary concentrations
-
Dairy products like yogurt and cheese
-
Fermented foods such as kefir and kombucha
-
Yeast-containing foods, including bread and some beers
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Nicotinamide Riboside
Nicotinamide riboside is generally considered well-tolerated, with a low risk of side effects based on current human research.
In clinical studies, daily intakes of up to 1,000 mg did not show harmful effects in participants (16). That said, most studies were short-term and involved small groups, so long-term safety data is still limited.
Some people have reported mild to moderate side effects, which may include:
-
Nausea
-
Fatigue
-
Headaches
-
Diarrhea
-
Stomach discomfort or indigestion
These effects appear to be uncommon and often dose-related. Anyone considering supplementation should speak with a healthcare professional, especially if using other NAD+ related products.
Nicotinamide Riboside Dosage
-v1766690749592.webp) There is no universally agreed standard dose for nicotinamide riboside. Most supplements provide between 250 mg and 300 mg per day, which aligns with amounts commonly used in early human studies.
There is no universally agreed standard dose for nicotinamide riboside. Most supplements provide between 250 mg and 300 mg per day, which aligns with amounts commonly used in early human studies.
Clinical trials have explored higher intakes, sometimes up to 1,000 mg per day, without major safety concerns. Regulatory guidance varies by region, and individual needs may differ based on age, health status, and existing supplement use.
Nicotinamide Riboside vs Other NAD+ Precursors
Several compounds can act as NAD+ precursors, but they differ in tolerance and research support.
-
Niacin: A vitamin B3 form that supports NAD+ production and cardiovascular markers (17). It often causes flushing and may place strain on the liver at higher doses (18).
-
NADH: The reduced form of NAD+. A meta-analysis found it less effective for supplementation compared to NR, NMN, or niacin (19).
-
NMN: A closely related NAD+ precursor that has gained attention as an alternative to NR. Research suggests it may also raise NAD+ levels, though direct comparisons in long-term human studies are still limited (20).
Final Words
Nicotinamide riboside is a vitamin B3 compound that supports NAD+ production, a process involved in cellular energy, repair, and normal aging pathways.
Early human studies suggest it may help maintain NAD+ levels with a relatively mild side effect profile, though more long-term research is still needed.
Food sources provide small amounts, while supplements offer a more concentrated option for those exploring NAD+ support. As with any supplement, informed use and professional guidance matter.
At Omre, we focus on evidence-led formulations that support healthy aging at the cellular level.
Our NMN + Resveratrol blend was developed with this same research-driven approach, combining well-studied NAD+ support with complementary compounds that fit into a balanced, thoughtful wellness routine.  Learn more about Omre NMN + Resveratrol and how it fits into a research-informed approach to NAD+ support.
Learn more about Omre NMN + Resveratrol and how it fits into a research-informed approach to NAD+ support.

About the medical reviewer
Dr Pedram Kordrostami, MD
Table of contents





